



Next: Packing Codes
Up: Centrally Defined Codes
Previous: Quantity Codes
Contents
Unit Codes
The unit codes are used in the
DESCRIP0.UNITS,
DESCRIP1.UNITS,
DESCRIP2.UNITS,
DESCRIP3.UNITS,
and DESCRIP.UNITS record fields. It
specifies the physical units for the data and its dimension. Each code
is stored in an integer at least 32 bits long. The bits are numbered
from 0 to 31, the least significant bit in the integer being number 0. Bits
29 to 31 define an index of eight possible forms of specifying units.
The format of the units code is as follows:
0 : Special and mathematical units
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(0,1){\line(1,0){32}}
\put(0,3){\line(1,0){32}}
\pu...
... \put(7,0){\makebox(9,1)[r]{16}}
\put(16,0){\makebox(16,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img58.gif)
- TYPE
- (bits 25 to 28, values 0 to 15) unit type
- CAT
- (bits 16 to 24, values 0 to 511) unit category
- UNIT
- (bits 0 to 15, values 0 to 65535) unit
1 : SI base units and dimensionless units from SI base units
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(0,1){\line(1,0){32}}
\put(0,3){\line(1,0){32}}
\pu...
...
\put(20,0){\makebox(8,1)[r]{4}}
\put(28,0){\makebox(4,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img59.gif)
- BASE
- (bits 25 to 28, values 0 to 15)
base unit (must be nonzero)
-
1 : length 

2 : mass 

3 : time 
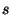
4 : temperature 
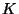
5 : amount of a substance 

6 : electrical current 
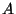
7 : luminous intensity 

8 : plane angle 

9 : solid angle 

- D
- (bit 24, values 0 to 1) dimensionless unit flag
-
- 0 : specifies a single base quantity
-
- 1 : specifies a ratio of quantities with the same BASE
-
- (e.g.,
 )
)
- EXPON
- (bits 20 to 23, values 0 to 15) exponent of the base
unit. Stored as 8+exponent (e.g.,
 would have EXPON = 10)
would have EXPON = 10)
- PREFIX
- (bits 12 to 19, values 0 to 255) prefix for the base
unit. Stored as 128+prefix (e.g.,
 would have PREFIX = 126).
Standard prefixes are:
would have PREFIX = 126).
Standard prefixes are:
-
| -18 |
atto |
a |
| -15 |
femto |
f |
| -12 |
pico |
p |
| -9 |
nano |
n |
| -6 |
micro |
 |
| -3 |
milli |
m |
| -2 |
centi |
c |
| -1 |
deci |
d |
| 1 |
deka |
da |
| 2 |
hecto |
h |
| 3 |
kilo |
k |
| 6 |
mega |
M |
| 9 |
giga |
G |
| 12 |
tera |
T |
| 15 |
peta |
P |
| 18 |
exa |
E |
- FAC
- (bits 4 to 11, values 0 to 255) for dimensionless quantities, the difference
between the exponent of the numerator and the exponent
of the denominator. Stored as
 difference
(e.g.,
difference
(e.g.,  would have FAC
would have FAC  )
)
- UNIT
- (bits 0 to 3, values 0 to 15) for dimensionless quantities, provides an
arbitrary index to distinguish between otherwise
similar quantities (e.g.,
 vs.
vs.  )
)
2 : SI approved named units
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(0,1){\line(1,0){32}}
\put(0,3){\line(1,0){32}}
\pu...
...
\put(20,0){\makebox(6,1)[r]{6}}
\put(26,0){\makebox(6,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img86.gif)
- BASE
- (bits 20 to 28, values 0 to 511)
base units. A bit array that specifies which
fundamental SI quantities make up the unit. From LSB
to MSB the bit position, the value to add, and the
basic units are (bit number, integer value, unit):
-
0 1 length
1 2 mass
2 4 time
3 8 temperature
4 16 amount of a substance
5 32 electrical current
6 64 luminous intensity
7 128 plane angle
8 256 solid angle
-
- (e.g.,
 so that BASE
so that BASE
 )
)
- PREFIX
- (bits 12 to 19, values 0 to 255) prefix for the base
unit. Stored as 128+prefix (e.g.,
 would have PREFIX = 126).
Standard prefixes are given above
would have PREFIX = 126).
Standard prefixes are given above
- CAT
- (bits 6 to 11, values 0 to 63) the category of the unit,
grouping quantities with the same physical meaning (e.g.,
 and
and  would be found in the same category: force)
would be found in the same category: force)
- UNIT
- (bits 0 to 5, values 0 to 63) provides an arbitrary index to distinguish
between quantities in the same category (e.g.,
 vs.
vs.  )
)
3 : General SI units in terms of base units with restrictions
4 : General non-SI units in terms of base units with restrictions
The structure of both of these forms is the same. Index 3 applies to the SI
combination of units, and index 4 applies to any combination of units that
include at least one non SI unit. There are certain restrictions in the
sizes of the various fields, depending on the number of base units that make
up the unit. Any unit that cannot be put into this form should use form 5
(General units without restrictions).
All cases have:
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(0,1){\line(1,0){12}}
\put(0,3){\line(1,0){12}}
\pu...
...
\put(0,0){\makebox(3,1)[r]{29}}
\put(3,0){\makebox(9,1)[r]{20}}
\end{picture}](img91.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(17,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{8}}
\put(24,0){\makebox(8,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img92.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(20,0){\makebox(5,1)[r]{7}}
\put(25,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img93.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(21,0){\makebox(4,1)[r]{7}}
\put(25,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img94.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(24,0){\makebox(3,1)[r]{5}}
\put(27,0){\makebox(5,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img95.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(22,0){\makebox(4,1)[r]{6}}
\put(26,0){\makebox(6,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img96.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(24,0){\makebox(3,1)[r]{5}}
\put(27,0){\makebox(5,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img95.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(19,0){\makebox(6,1)[r]{7}}
\put(25,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img97.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(20,0){\makebox(5,1)[r]{7}}
\put(25,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img93.gif)
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(12,1){\line(1,0){20}}
\put(12,3){\line(1,0){20}}
\...
...
\put(21,0){\makebox(4,1)[r]{7}}
\put(25,0){\makebox(7,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img94.gif)
- BASE
- (bits 20 to 28, values 0 to 511)
base units. A bit array that specifies which
fundamental SI quantities make up the unit. From LSB
to MSB the bit position, the value to add, and the
basic units are (bit number, integer value, unit):
-
0 1 length
1 2 mass
2 4 time
3 8 temperature
4 16 amount of a substance
5 32 electrical current
6 64 luminous intensity
7 128 plane angle
8 256 solid angle
-
- (e.g.,
 so that BASE
so that BASE
 )
)
- E
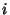
- the exponents of the base units. Note that a zero
exponent is not included, since it is assumed that the base unit exists if
specified. The size and value of the field is variable, depending on the number of
base units as follows:
-
| base num |
bits |
range |
exponents |
| 1 |
15 to 19 |
0 to 31 |
-16 to 16 |
| 2 |
12 to 19 |
0 to 15 |
-8 to 8 |
| 3 |
11 to 19 |
0 to 7 |
-4 to 4 |
| 4 |
8 to 19 |
0 to 7 |
-4 to 4 |
| 5 |
10 to 19 |
0 to 3 |
-2 to 2 |
| 6 |
8 to 19 |
0 to 3 |
-2 to 2 |
| 7 |
13 to 19 |
0 to 1 |
-1 or 1 |
| 8 |
12 to 19 |
0 to 1 |
-1 or 1 |
| 9 |
11 to 19 |
0 to 1 |
-1 or 1 |
- CAT
- the category of the unit, grouping quantities with the
same physical meaning (e.g.,
 and
and  would be found in the same
category: velocity). The size and value of the field is variable depending on
the number of base units as follows:
would be found in the same
category: velocity). The size and value of the field is variable depending on
the number of base units as follows:
-
| base num |
bits |
range |
|
| 1 |
8 to 14 |
0 to 127 |
|
| 2 |
7 to 11 |
0 to 31 |
|
| 3 |
7 to 10 |
0 to 15 |
|
| 4 |
5 to 7 |
0 to 7 |
|
| 5 |
6 to 9 |
0 to 15 |
|
| 6 |
5 to 7 |
0 to 7 |
|
| 7 |
7 to 12 |
0 to 63 |
|
| 8 |
7 to 11 |
0 to 31 |
|
| 9 |
7 to 10 |
0 to 15 |
|
- UNIT
- provides an arbitrary index to distinguish between
quantities in the same category (e.g.,
 vs.
vs.  ). The size and value of
the field is variable depending on the number of base units as follows:
). The size and value of
the field is variable depending on the number of base units as follows:
-
| base num |
bits |
range |
|
| 1 |
0 to 7 |
0 to 255 |
|
| 2 |
0 to 6 |
0 to 127 |
|
| 3 |
0 to 6 |
0 to 127 |
|
| 4 |
0 to 4 |
0 to 31 |
|
| 5 |
0 to 5 |
0 to 63 |
|
| 6 |
0 to 4 |
0 to 31 |
|
| 7 |
0 to 6 |
0 to 127 |
|
| 8 |
0 to 6 |
0 to 127 |
|
| 9 |
0 to 6 |
0 to 127 |
|
5 : General units with no restrictions
![\begin{picture}(32,3)
\put(0,1){\line(1,0){32}}
\put(0,3){\line(1,0){32}}
\pu...
... \put(13,0){\makebox(10,1)[r]{9}}
\put(23,0){\makebox(9,1)[r]{0}}
\end{picture}](img100.gif)
- BASE
- (bits 20 to 28, values 0 to 511)
base units. A bit array that specifies which
fundamental SI quantities make up the unit. From LSB
to MSB the bit position, the value to add, and the
basic units are (bit number, integer value, unit):
-
0 1 length
1 2 mass
2 4 time
3 8 temperature
4 16 amount of a substance
5 32 electrical current
6 64 luminous intensity
7 128 plane angle
8 256 solid angle
-
- (e.g.,
 so that BASE
so that BASE  )
)
- T
- (bit 19, values 0 to 1) SI unit indicator
-
- 0 : SI unit
-
- 1 : non-SI unit
- CAT
- (bits 9 to 18, values 0 to 1023) the category of the
unit, grouping quantities with the same physical meaning
(e.g.,
 and
and  would be found in the same category: velocity)
would be found in the same category: velocity)
- UNIT
- (bits 0 to 8, values 0 to 511) provides an arbitrary
index to distinguish between quantities in the same category
(e.g.,
 vs.
vs.  )
)
7 : Locally defined units
These units are site-defined as specified in Section A.2.5.




Next: Packing Codes
Up: Centrally Defined Codes
Previous: Quantity Codes
Contents
Eric Nash
2003-09-25
![]()
![]()





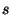

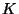



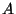






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()