



Next: Site Identifier Codes
Up: Centrally Defined Codes
Previous: Centrally Defined Codes
Contents
Data Format Codes
The data format codes are used in the
OBJDESC.COMCOD,
DESCRIP0.DATFMT,
DESCRIP1.DESFMT, DESCRIP2.DESFMT,
DESCRIP3.DESFMT, DESCRIP.DESFMT,
PROCFORM.PRCFMT, PAKSPEC.DPAKFMT,
PAKFORM.PAKFMT, and COMPFORM.COMPFMT record
fields. These codes are integer values at least 32 bits long
(because the codes are defined bit by bit, it is irrelevant whether
these integers are considered to be signed or unsigned). The
integer is expressed as a sequence of eight 4-bit nybbles, numbered from 0 to
7, the most significant nybble in the integer being number 0. The
codes are structured in such a way that they can be interpreted by
inspecting a hexadecimal printout.
The nybble specifications are as follows (LSB = Least Significant Bit,
MSB = Most Significant Bit):
0 : Numeric types
1 : logical or Boolean

- size
- 0 : same size as short integer
1 : same size as long integer
- true-value
- 0 : LSB is clear (0)
1 : LSB is set (1)
2 : MSB is set (1)
3 : MSB is clear (0)
- false-value
- 0 : LSB is clear (0)
1 : LSB is set (1)
2 : MSB is set (1)
3 : MSB is clear (0)
2 : byte

- sign
- 0 : unsigned
1 : signed
3 : integer

- sign
- 0 : unsigned
1 : signed
- size
- 0 : short
1 : long
4 : floating-point

- size
- 0 : single precision
1 : double precision
2 : extended precision
3 : super-extended precision
5 : complex floating-point

- size
- 0 : single precision
1 : double precision
2 : extended precision
3 : super-extended precision
1 : Character types
Note that the string lengths given below include only the characters in
the string proper, not including any header or trailer bytes.
0 : XDR
string
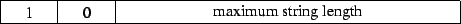
1 : fixed-length sequence of characters with no string length

2 : sequence of characters preceded by string length
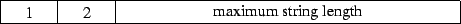
3 : sequence of characters followed by a null character
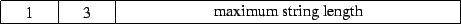
4 : XDR counted
string (IDL extension)
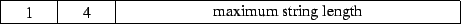
2 : Structure types
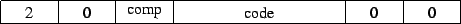
- comp
- number of components in the structure
- code
- unique code to identify the structure
-
- 0 :
- a pair of bytes in (MSB, LSB) order which comprise a short
integer
- 1 :
- a quadruplet of long integers (used as nodes for AUDIT.TREE)
The following are common examples of the data format codes:
- Hex
-
- Decimal
-
- 01010000
-
- 16842752
- logical with length of short integer (IDL logicals)
true = 1, false = 0
- 02000000
-
- 33554432
- unsigned byte
- 02100000
-
- 34603008
- signed byte
- 03000000
-
- 50331648
- unsigned short integer
- 03100000
-
- 51380224
- signed short integer
- 03010000
-
- 50397184
- unsigned long integer
- 03110000
-
- 51445760
- signed long integer
- 04000000
-
- 67108864
- single precision floating-point
- 04100000
-
- 68157440
- double precision floating-point
- 04200000
-
- 69206016
- extended precision floating-point
- 05000000
-
- 83886080
- single precision complex
- 05100000
-
- 84934656
- double precision complex
- 05200000
-
- 85983232
- extended precision complex
- 05300000
-
- 87031808
- super-extended precision complex
- 10000001
-
- 268435457
- XDR
string, a maximum of one character long
- 10000050
-
- 268435536
- XDR
string, a maximum of 80 characters long
- 11000001
-
- 285212673
- fixed-length string of 1 character
- 11000050
-
- 285212752
- fixed-length string of 80 characters
- 13000050
-
- 318767184
- Null-terminates string; max length is 80 characters
- 20200000
-
- 538968064
- short integer (signed) from a 2-byte base (MSB,LSB)
- 20300100
-
- 540016896
- four unsigned long integers (used as nodes in the
AUDIT.TREE structure)




Next: Site Identifier Codes
Up: Centrally Defined Codes
Previous: Centrally Defined Codes
Contents
Eric Nash
2003-09-25
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()